Creating a safe and healthy work environment is not only a legal obligation but also a crucial factor in maintaining employee satisfaction, reducing costs, and improving productivity. Whether you’re running a small business or managing a large enterprise, implementing best practices for health and safety in the workplace is essential for long-term success. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the best strategies employers can adopt to create a safer workplace, comply with regulations, and promote a culture of health and safety among their teams.
Why Workplace Health and Safety Matters

Protecting Employees and Reducing Injuries
The primary goal of health and safety protocols is to protect employees from injury, illness, and hazards. This not only improves morale but also leads to lower absenteeism and fewer workers’ compensation claims.
Legal and Financial Implications
Failing to comply with health and safety regulations can result in hefty fines, lawsuits, and even criminal charges in severe cases. Being proactive helps mitigate these risks.
Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency
When employees feel safe, they are more likely to focus on their work and perform at their best. A safe workplace leads to fewer disruptions and a more productive workforce.
Legal Obligations for Employers

Understanding National and Local Regulations
Employers must be familiar with occupational health and safety (OHS) laws and regulations, such as OSHA in the U.S. or HSE in the U.K. These laws outline the minimum standards that must be met in every industry.
Keeping Up with Changes
Regulations can change due to new research, technology, or global health crises (like COVID-19). Employers should regularly review updates to ensure compliance.
Providing Necessary Documentation
Maintaining proper records—such as risk assessments, incident reports, and safety audits—is critical for legal compliance and internal safety reviews.
Best Practices for Workplace Health and Safety
1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Identifying and evaluating risks is the foundation of a robust health and safety policy.
Steps to Conduct a Risk Assessment:
- Identify potential hazards.
- Determine who may be harmed and how.
- Evaluate the risks and decide on precautions.
- Record findings and implement solutions.
- Review and update regularly.
2. Create a Comprehensive Health and Safety Policy
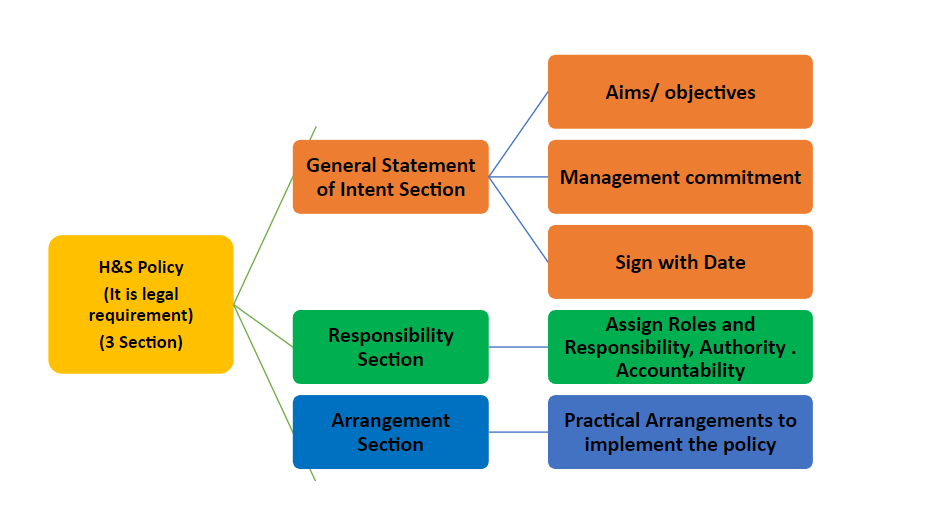
A clear policy helps establish guidelines and expectations for all employees.
Key Components of a Policy:
- Statement of intent
- Responsibilities of management and staff
- Arrangements for health and safety implementation
3. Offer Training and Education
Training ensures employees understand their responsibilities and how to perform tasks safely.
Effective Training Methods:
- Onboarding sessions
- Regular workshops
- Online modules and assessments
- Emergency drills and simulations
4. Promote Open Communication
Encourage employees to report hazards, near-misses, or suggestions without fear of retaliation.
Tools for Communication:
- Suggestion boxes
- Safety meetings
- Anonymous reporting platforms
5. Provide the Right Tools and Equipment
Employees should have access to the proper equipment to perform their tasks safely.
Examples Include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Ergonomic office furniture
- Machine guards and safety signs
Industry-Specific Safety Practices
Construction
- Use scaffolding and fall protection.
- Conduct daily equipment inspections.
- Enforce proper use of helmets and boots.
Healthcare
- Follow strict hygiene and infection control protocols.
- Train staff on handling hazardous substances.
- Provide mental health support for high-stress roles.
Manufacturing
- Install emergency stop mechanisms.
- Control exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Monitor machinery to prevent overheating or malfunction.
Office Environments
- Encourage regular breaks to prevent eye strain.
- Maintain proper lighting and ventilation.
- Promote desk ergonomics and posture awareness.
Fostering a Culture of Health and Safety
Lead by Example
When leadership prioritizes safety, employees are more likely to follow suit. Executives and managers should model safety-conscious behaviors.
Recognize and Reward Safe Behavior
Create incentives for employees who consistently adhere to safety practices. Recognition can be in the form of bonuses, awards, or public acknowledgment.
Involve Employees in Safety Initiatives
Empower your team by involving them in the decision-making process. Form safety committees or task forces to assess and improve workplace practices.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Implement Incident Reporting Systems
Track accidents, near misses, and unsafe conditions to identify patterns and prevent future occurrences.
Use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Metrics like incident rates, sick leave statistics, and employee feedback can offer valuable insight into the effectiveness of your safety program.
Conduct Regular Audits
Periodic audits ensure policies are being followed and help uncover areas for improvement. Audits should be both internal and external.
Mental Health and Wellbeing at Work
Importance of Mental Health in the Workplace
A healthy mind is just as important as physical safety. Stress, burnout, and anxiety can impact productivity and employee retention.
Supportive Practices for Employers:
- Offer Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs)
- Create a flexible work environment
- Provide mental health days and resources
- Train managers to recognize signs of mental health issues
Technology’s Role in Workplace Safety

Safety Management Software
Software tools can automate risk assessments, training, incident reporting, and compliance tracking.
Wearable Safety Tech
Devices like smart helmets or vests can monitor vital signs, detect falls, or warn about environmental hazards.
Virtual and Augmented Reality
VR and AR technologies can provide immersive safety training experiences, particularly useful for high-risk industries like construction and manufacturing.
Adapting Health and Safety Post-Pandemic
Enhanced Cleaning Protocols
Employers must now consider regular sanitation of shared spaces, desks, and high-touch surfaces.
Hybrid Work Models
Flexible work arrangements can help reduce workplace density and the spread of illness.
Health Screenings and Policies
Encourage self-monitoring, temperature checks, and clear policies around sick leave and working from home when ill.
Also Read : 7 Most Effective Home Workouts For Any Fitness Level!
Conclusion
Maintaining a safe and healthy work environment is an ongoing commitment that benefits both employers and employees. By implementing best practices—from risk assessments and training to open communication and mental health support—employers can build a culture where safety is ingrained in every aspect of operations. Remember, a strong health and safety strategy not only protects your people but also boosts morale, productivity, and your organization’s reputation. In today’s fast-paced and evolving work environment, staying proactive and continuously improving your safety practices is the key to long-term success.
FAQs
What is the most important aspect of workplace health and safety?
The most critical aspect is identifying and mitigating risks through regular assessments and employee training. Prevention is always better than cure.
How often should risk assessments be conducted?
Risk assessments should be done at least annually or whenever there is a significant change in work processes, equipment, or regulations.
What are some common workplace hazards?
Common hazards include slips and falls, ergonomic injuries, chemical exposure, electrical hazards, and mental health challenges such as stress or burnout.
Are employers legally required to provide safety training?
Yes, in most countries, employers are legally obligated to provide training to ensure employees can perform their tasks safely.
How can small businesses improve health and safety with limited budgets?
Start with low-cost initiatives like clear signage, basic PPE, online training modules, and encouraging open communication. Partnering with local health and safety organizations can also provide resources and guidance.

